G major triad bass clef – Unveiling the G major triad in bass clef, we embark on a musical odyssey that unravels its significance in the tapestry of music theory and practical applications. From its fundamental structure to its harmonic functions and practical uses, this guide delves into the depths of this essential musical building block.
Music Theory Basics

Triads
A triad is a fundamental musical concept that refers to a set of three notes played simultaneously. Triads form the foundation of harmony and are used extensively in music across genres.
Major Triads
A major triad is a specific type of triad that consists of the root note, the major third (four half steps above the root), and the perfect fifth (seven half steps above the root). The root is the fundamental note of the triad and determines its overall pitch.
The major third adds brightness and fullness to the sound, while the perfect fifth provides stability and closure.
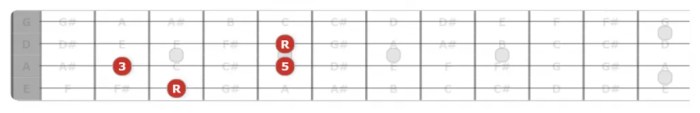
G Major Triad in Bass Clef

In the bass clef, the G major triad consists of the notes G, B, and D. These notes are arranged in a specific order, with G as the root note, B as the third, and D as the fifth.
Fingerings for Playing the G Major Triad
The fingerings for playing the G major triad in bass clef on the piano are as follows:
- G: Left-hand thumb (1)
- B: Left-hand index finger (2)
- D: Left-hand middle finger (3)
Diagram of the G Major Triad
The following diagram shows the G major triad in bass clef:

Harmonic Functions of the G Major Triad
The G major triad is a versatile chord that can serve various harmonic functions in different musical contexts. As a tonic chord, it establishes the tonal center and provides a sense of stability. In this role, the G major triad is often used as the first and last chord in a piece of music.
Subdominant Function
When used as a subdominant chord, the G major triad creates a sense of movement and anticipation. It suggests the progression to the dominant chord, which ultimately resolves to the tonic. In chord progressions, the G major triad is commonly preceded by the C major chord and followed by the D major chord.
Dominant Function, G major triad bass clef
In certain harmonic contexts, the G major triad can also act as a dominant chord. This occurs when it is used to create a sense of tension and anticipation before resolving to a tonic chord. In this role, the G major triad is often preceded by the D major chord and followed by the C major chord.
Practical Applications of the G Major Triad
The G major triad is a versatile harmonic tool used extensively in various musical genres and styles. Its bright and cheerful sound makes it a popular choice for creating uplifting and energetic melodies.
Examples of Usage
-
-*Classical Music
The G major triad forms the basis of numerous classical compositions, including symphonies, concertos, and sonatas. It is often used as a tonic chord, providing a sense of stability and resolution.
-*Jazz
G major triad bass clef is a fundamental musical concept used in various genres. For instance, in the captivating Spanish ballad “El Romance del Rey Moro” el romance del rey moro , the G major triad bass clef forms the harmonic foundation for the song’s enchanting melody.
In jazz, the G major triad is commonly employed in improvisation and soloing. Jazz musicians use it to create melodic lines, chord progressions, and harmonic embellishments.
-*Pop Music
Pop songs often feature the G major triad as a foundational chord. Its uplifting and optimistic sound makes it well-suited for creating catchy melodies and choruses.
-*Rock Music
The G major triad is frequently used in rock music as a power chord, combining the root, perfect fifth, and octave. It provides a solid harmonic foundation for guitar-driven riffs and solos.
Exercises and Etudes
-
-*Triad Inversions
Practice playing the G major triad in all three inversions (root position, first inversion, and second inversion) to develop finger dexterity and harmonic awareness.
-*Chord Progressions
Compose simple chord progressions using the G major triad as a starting point. Experiment with different bass notes and rhythms to create variations and explore harmonic possibilities.
-*Melodic Lines
Create melodies that incorporate the G major triad. Use the notes of the triad as stepping stones or melodic targets to create cohesive and pleasing phrases.
Key Uses and Applications
|
- *Key Use |
- *Application |
|—|—|| Tonic Chord | Establishes the tonal center and provides stability || Dominant Chord | Creates tension and resolution in chord progressions || Subdominant Chord | Provides contrast and leads back to the tonic || Harmony for Melodies | Supports and enhances melodic lines || Chord Inversions | Adds harmonic variety and interest |
Advanced Concepts

Beyond the basic triad, the G major triad can be extended into richer harmonic structures. These extended forms expand the tonal possibilities and offer greater flexibility in improvisation and composition.
G Major 7th Chord
The G major 7th chord is formed by adding the seventh scale degree, B, to the G major triad. This intervallic structure creates a more complex and dissonant sound. The G major 7th chord is commonly used in jazz, blues, and pop music.
G Major 9th Chord
The G major 9th chord is further extended by adding the ninth scale degree, D. This chord adds a bright and airy quality to the harmony. It is often used in jazz improvisation and modern classical music.
Jazz Improvisation and Harmonic Analysis
The G major triad and its extended forms play a crucial role in jazz improvisation and harmonic analysis. Jazz musicians often use these chords as a starting point for improvisation, exploring different melodic and rhythmic variations. Harmonic analysis, on the other hand, utilizes these chords to understand the underlying harmonic structure of jazz compositions.
Historical and Cultural Significance
The G major triad has held a significant place in Western music throughout history. It is one of the most fundamental chords in tonal music, appearing in countless compositions from the Baroque era to the present day. The triad’s simple and consonant sound has made it a favorite for composers seeking to evoke a sense of stability and resolution.
Questions Often Asked: G Major Triad Bass Clef
What is the root note of the G major triad?
G
How is the G major triad played in bass clef on the piano?
Using the left hand, play G with the thumb, B with the middle finger, and D with the pinky finger.