Gaseous ammonia chemically reacts with oxygen, embarking on a captivating journey that unveils the intricate dance between these two fundamental substances. Delving into their physical and chemical properties, we unravel the secrets of their molecular structures, bonding, and reactivity, setting the stage for a remarkable chemical transformation.
As ammonia and oxygen collide, a balanced chemical equation emerges, revealing the intricate choreography of their interaction. The reaction mechanism and the role of a catalyst come into play, orchestrating the conversion of reactants into products. Temperature, pressure, and concentration emerge as crucial factors, influencing the kinetics and equilibrium of this fascinating reaction.
Gaseous Ammonia Properties: Gaseous Ammonia Chemically Reacts With Oxygen
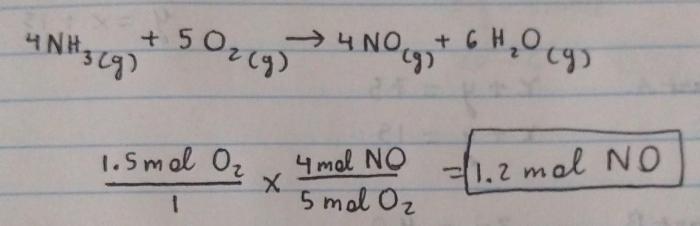
Gaseous ammonia (NH3) is a colorless, pungent gas with a molecular weight of 17.03 g/mol. It is a highly reactive compound that readily reacts with acids and bases.
Molecular Structure and Bonding
Ammonia has a trigonal pyramidal molecular structure, with the nitrogen atom at the apex and the three hydrogen atoms at the base. The nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons, which gives the molecule its characteristic polarity.
Solubility, Density, and Reactivity, Gaseous ammonia chemically reacts with oxygen
Ammonia is highly soluble in water, with a solubility of 899 g/L at 25 °C. It is also soluble in other polar solvents, such as methanol and ethanol. Ammonia has a density of 0.771 g/L at 25 °C and is less dense than air.
Oxygen Properties

Oxygen (O2) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas with a molecular weight of 32.00 g/mol. It is a highly reactive element that is essential for life.
Molecular Structure and Bonding
Oxygen has a diatomic molecular structure, with two oxygen atoms bonded together by a double bond. The oxygen-oxygen bond is very strong, with a bond energy of 498 kJ/mol.
Solubility, Density, and Reactivity, Gaseous ammonia chemically reacts with oxygen
Oxygen is slightly soluble in water, with a solubility of 49.5 mg/L at 25 °C. It is also soluble in other polar solvents, such as methanol and ethanol. Oxygen has a density of 1.429 g/L at 25 °C and is denser than air.
Chemical Reaction between Ammonia and Oxygen
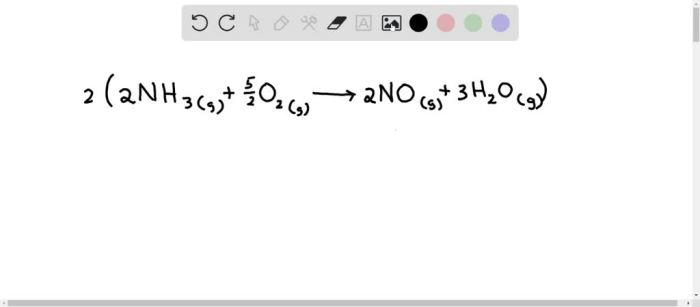
Ammonia and oxygen react to form nitrogen monoxide (NO) and water (H2O) according to the following balanced chemical equation:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
The reaction is exothermic, releasing 905 kJ/mol of heat.
Reaction Mechanism and Catalyst
The reaction proceeds via a free radical mechanism, involving the formation of hydroxyl radicals (OH) and hydrogen atoms (H). A catalyst, such as platinum or rhodium, is required to initiate the reaction.
Reaction Conditions
The reaction is typically carried out at high temperatures (800-1000 °C) and pressures (1-10 atm). The concentration of ammonia and oxygen in the reaction mixture also affects the rate of reaction.
Reaction Products
The products of the reaction between ammonia and oxygen are nitrogen monoxide (NO) and water (H2O).
Nitrogen Monoxide (NO)
Nitrogen monoxide is a colorless, toxic gas with a molecular weight of 30.01 g/mol. It is a highly reactive compound that readily reacts with other molecules to form nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
Water (H2O)
Water is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless liquid with a molecular weight of 18.02 g/mol. It is the most abundant compound on Earth and is essential for life.
Industrial Applications
The reaction between ammonia and oxygen is used in the industrial production of nitric acid (HNO3) and fertilizers.
Nitric Acid Production
Nitric acid is produced by the Ostwald process, which involves the catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen monoxide (NO), followed by the reaction of NO with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide (NO2). The NO2 is then absorbed in water to form nitric acid.
Fertilizer Production
Ammonia is used as a fertilizer, either directly or in the form of ammonium salts. Ammonium salts are produced by the reaction of ammonia with acids, such as sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid.
Popular Questions
What are the physical properties of gaseous ammonia?
Gaseous ammonia is a colorless, pungent gas with a boiling point of -33.34 °C and a melting point of -77.73 °C. It is highly soluble in water and has a density of 0.731 g/L at 0 °C.
What is the molecular structure of oxygen?
Oxygen exists as a diatomic molecule, O2, with each oxygen atom bonded to the other by a double bond. The bond length is 121 pm, and the bond energy is 498 kJ/mol.
What are the industrial applications of the reaction between ammonia and oxygen?
The reaction between ammonia and oxygen is used to produce nitric acid, which is a key component in the production of fertilizers and explosives. It is also used to produce fertilizers directly, such as ammonium nitrate and urea.