Irwin is a monopoly seller of specialty bearings, dominating the market with its unique offerings. This dominance has sparked interest in understanding the implications of a monopoly in this industry, including its impact on pricing, competition, and consumer welfare.
The specialty bearings market exhibits high barriers to entry, allowing Irwin to maintain its position as the sole supplier. This has enabled the company to set prices above marginal cost, influencing market dynamics and raising questions about market efficiency.
Market Structure
A monopoly is a market structure characterized by the presence of a single seller who has complete control over the supply of a particular product or service. This gives the monopolist significant market power, allowing it to influence prices and output to maximize its profits.
Monopolies arise due to various factors, including high barriers to entry, economies of scale, and government-granted exclusive rights (such as patents or licenses). These barriers prevent other firms from entering the market and competing with the monopolist.
Some examples of other monopoly markets include utilities (e.g., water, electricity), telecommunications, and certain pharmaceuticals.
Demand and Supply
The demand for specialty bearings is influenced by various factors, including the demand from end-use industries (e.g., automotive, aerospace, manufacturing) and the specifications of the bearings required for different applications.
The supply of specialty bearings is dominated by Irwin, which is the sole supplier in the market. Irwin’s production costs and economies of scale give it a significant advantage over potential entrants.
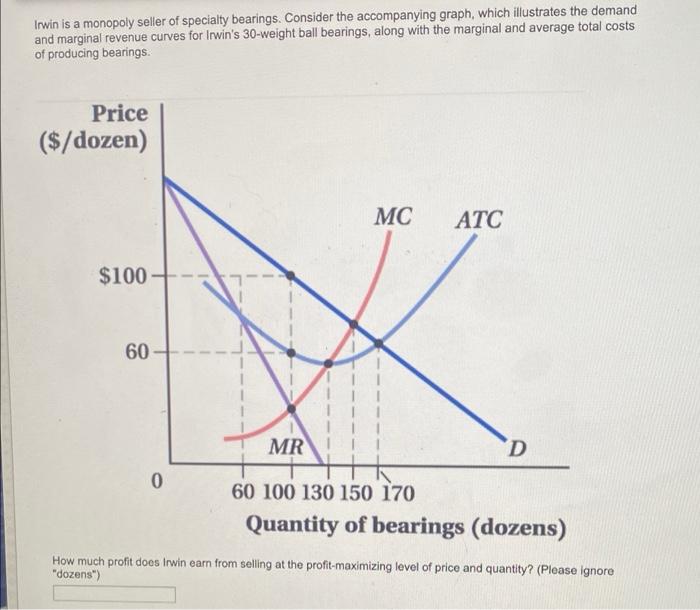
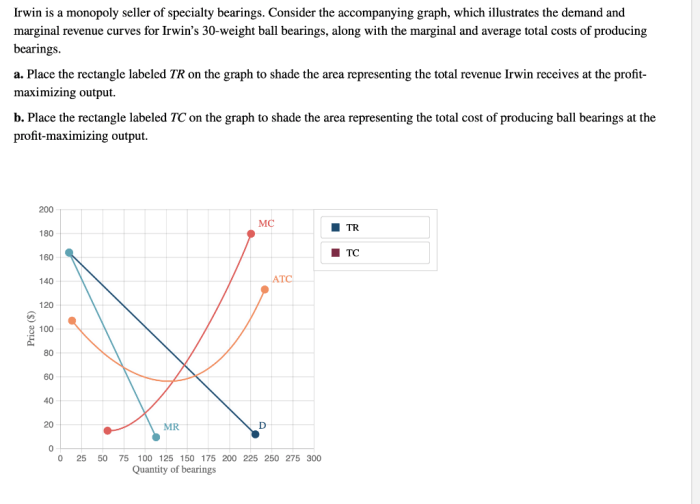
The supply and demand graph below illustrates the market equilibrium and the impact of Irwin’s monopoly power. The equilibrium price (P*) is set above the marginal cost (MC), resulting in consumer surplus (CS) and producer surplus (PS).

Pricing and Output
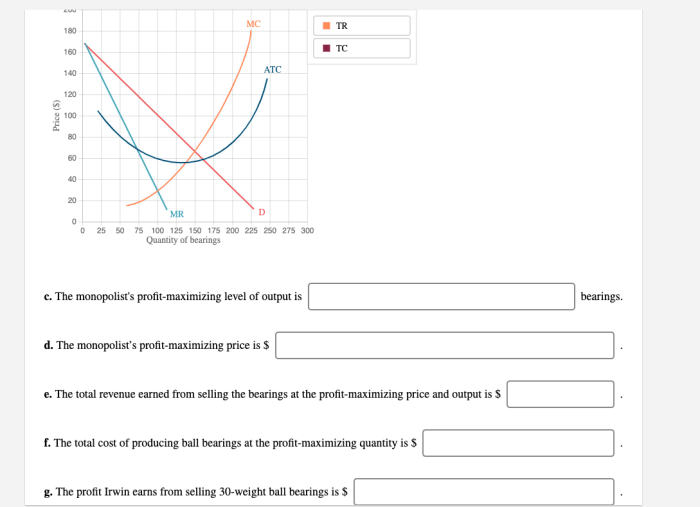
Irwin’s monopoly power allows it to set prices above marginal cost, maximizing its profits. The monopolist’s pricing strategy is influenced by factors such as market demand, production costs, and regulatory constraints.
The impact of Irwin’s pricing on consumer surplus and producer surplus depends on the elasticity of demand. If demand is inelastic, consumers have limited alternatives and are willing to pay a higher price. This allows Irwin to maximize its profits while minimizing consumer surplus.
Barriers to Entry

The specialty bearings market is characterized by high barriers to entry that prevent other firms from entering and competing with Irwin.
- Patents: Irwin holds patents on the design and manufacturing processes of its specialty bearings, giving it exclusive rights to produce and sell these products.
- Economies of Scale: Irwin has invested heavily in specialized equipment and production facilities, resulting in significant economies of scale that make it difficult for new entrants to match its efficiency and low costs.
- Market Share: Irwin’s dominant market share and established customer base create a significant barrier to entry for new firms trying to gain a foothold in the market.
Regulation and Competition Policy
Government regulation plays a crucial role in the specialty bearings market, aiming to balance Irwin’s monopoly power with the interests of consumers and the overall market efficiency.
Price controls and antitrust enforcement are common regulatory measures used to prevent excessive pricing and maintain a competitive market environment.
Alternative competition policies, such as encouraging innovation and supporting new entrants, can also promote market efficiency and consumer welfare.
General Inquiries: Irwin Is A Monopoly Seller Of Specialty Bearings
What factors contribute to Irwin’s monopoly power?
Irwin’s monopoly power stems from high barriers to entry, including patents, economies of scale, and its established market share.
How does Irwin’s monopoly affect consumer surplus?
As a monopolist, Irwin can set prices above marginal cost, reducing consumer surplus compared to a competitive market.
What role does government regulation play in the specialty bearings market?
Government regulation aims to address concerns related to monopoly power, such as price controls or antitrust enforcement, to promote market efficiency and consumer welfare.