The drawing shows a skateboarder moving at 5.4 m/s sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The drawing captures the essence of skateboarding, a sport that combines athleticism, creativity, and a touch of daring.
As we delve into the scientific principles that govern skateboarding, we will explore the interplay of speed, velocity, acceleration, friction, momentum, and energy, unraveling the secrets behind the skateboarder’s motion.
The skateboarder’s journey begins with an understanding of speed and velocity. Speed, a scalar quantity, measures the rate at which the skateboarder covers distance, while velocity, a vector quantity, incorporates both speed and direction. In the context of skateboarding, speed alone does not provide a complete picture of the skateboarder’s motion; velocity, with its directional component, allows us to determine the skateboarder’s trajectory and path.
Speed and Velocity
Speed is the rate at which an object covers distance, while velocity is the rate at which an object covers distance in a specific direction. In skateboarding, speed is typically measured in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h), while velocity is measured in meters per second in a specific direction (e.g.,
5.4 m/s north).
Examples
- A skateboarder moving at 5.4 m/s has a speed of 5.4 m/s.
- A skateboarder moving at 5.4 m/s north has a velocity of 5.4 m/s north.
Distance and Time
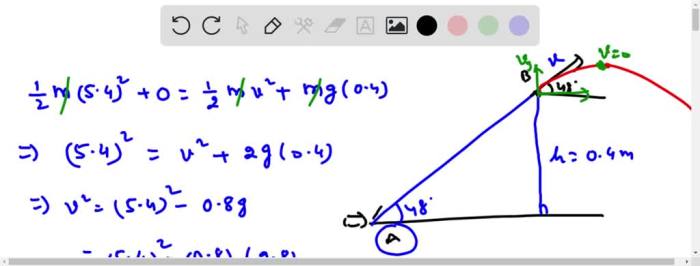
Distance is the total length of the path traveled by an object, while time is the duration of the object’s motion. In skateboarding, distance is typically measured in meters (m) or kilometers (km), while time is measured in seconds (s) or minutes (min).
Formula
Distance = Speed × Time
Example
A skateboarder moving at 5.4 m/s for 10 seconds will travel a distance of 54 meters.
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time. In skateboarding, acceleration is typically measured in meters per second squared (m/s²). Positive acceleration indicates that the object is speeding up, while negative acceleration indicates that the object is slowing down.
Effects on Skateboarding
- Positive acceleration allows skateboarders to gain speed and perform tricks.
- Negative acceleration helps skateboarders to slow down and stop.
Friction
Friction is the force that opposes the motion of an object. In skateboarding, friction is caused by the contact between the skateboard’s wheels and the ground. Friction can be reduced by using smoother wheels or bearings, or increased by using rougher wheels or surfaces.
Effects on Skateboarding
- Friction slows down skateboarders.
- Friction helps skateboarders to control their speed and direction.
Momentum
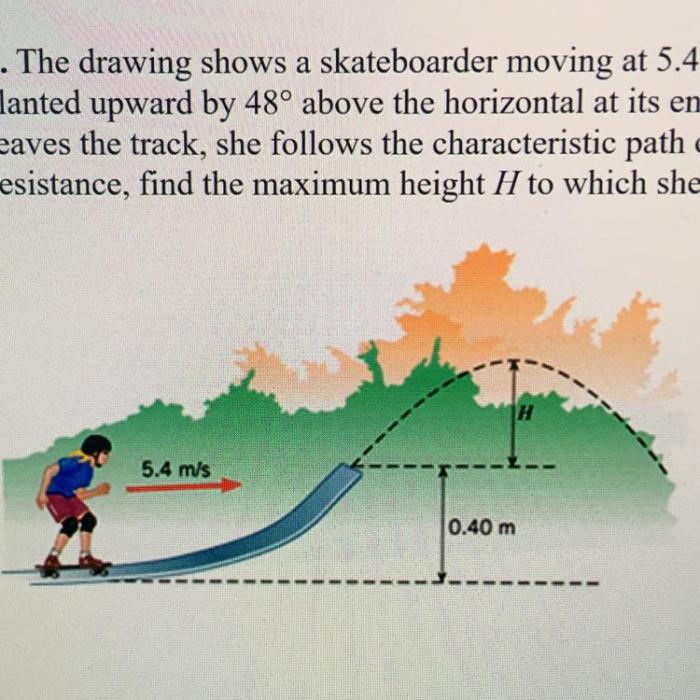
Momentum is a measure of an object’s mass and velocity. In skateboarding, momentum is important because it determines the amount of force required to stop or redirect a skateboarder.
Conservation of Momentum
In a closed system, momentum is conserved, meaning that the total momentum of all objects in the system remains constant.
Energy: The Drawing Shows A Skateboarder Moving At 5.4 M/s
Energy is the ability to do work. In skateboarding, energy is involved in every aspect of the activity, from the initial push to the final landing.
Forms of Energy
- Kinetic energy: the energy of motion
- Potential energy: the energy of position
- Thermal energy: the energy of heat
Transfer and Transformation of Energy, The drawing shows a skateboarder moving at 5.4 m/s
Energy is constantly being transferred and transformed in skateboarding. For example, when a skateboarder pushes off the ground, kinetic energy is transferred from the skateboarder’s legs to the skateboard. When the skateboard rolls, the kinetic energy is transformed into thermal energy due to friction.
Expert Answers
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is a scalar quantity that measures the rate at which an object covers distance, while velocity is a vector quantity that incorporates both speed and direction.
How does acceleration affect the motion of a skateboarder?
Acceleration is the rate at which an object’s velocity changes. In skateboarding, acceleration can be used to increase or decrease the skateboarder’s speed or to change their direction.
What is the role of friction in skateboarding?
Friction is a force that opposes the motion of an object. In skateboarding, friction acts as a brake, slowing the skateboarder down. However, friction can also be harnessed to control the skateboard’s movement.